Beginner Node.js Interview Questions
1. What is Node.js? Where can you use it?
Node.js is an open-source, cross-platform JavaScript runtime environment and library to run web applications outside the client’s browser. It is used to create server-side web applications.
Node.js is perfect for data-intensive applications as it uses an asynchronous, event-driven model. You can use I/O intensive web applications like video streaming sites. You can also use it for developing: Real-time web applications, Network applications, General-purpose applications, and Distributed systems.
2. Why use Node.js?
Node.js makes building scalable network programs easy. Some of its advantages include:
- It is generally fast
- It rarely blocks
- It offers a unified programming language and data type
- Everything is asynchronous
- It yields great concurrency
3. How does Node.js work?
A web server using Node.js typically has a workflow that is quite similar to the diagram illustrated below. Let’s explore this flow of operations in detail.

- Clients send requests to the webserver to interact with the web application. Requests can be non-blocking or blocking:
- Querying for data
- Deleting data
- Updating the data
- Node.js retrieves the incoming requests and adds those to the Event Queue
- The requests are then passed one by one through the Event Loop. It checks if the requests are simple enough not to require any external resources
- The Event Loop processes simple requests (non-blocking operations), such as I/O Polling, and returns the responses to the corresponding clients
A single thread from the Thread Pool is assigned to a single complex request. This thread is responsible for completing a particular blocking request by accessing external resources, such as computation, database, file system, etc.
Once the task is carried out completely, the response is sent to the Event Loop that sends that response back to the client.
4. Why is Node.js Single-threaded?
Node.js is single-threaded for async processing. By doing async processing on a single-thread under typical web loads, more performance and scalability can be achieved instead of the typical thread-based implementation.
5. If Node.js is single-threaded, then how does it handle concurrency?
The Multi-Threaded Request/Response Stateless Model is not followed by the Node JS Platform, and it adheres to the Single-Threaded Event Loop Model. The Node JS Processing paradigm is heavily influenced by the JavaScript Event-based model and the JavaScript callback system. As a result, Node.js can easily manage more concurrent client requests. The event loop is the processing model’s beating heart in Node.js.
6. Explain callback in Node.js.
A callback function is called after a given task. It allows other code to be run in the meantime and prevents any blocking. Being an asynchronous platform, Node.js heavily relies on callback. All APIs of Node are written to support callbacks.
7. What are the advantages of using promises instead of callbacks?
- The control flow of asynchronous logic is more specified and structured.
- The coupling is low.
- We’ve built-in error handling.
- Improved readability.
8. How would you define the term I/O?
- The term I/O is used to describe any program, operation, or device that transfers data to or from a medium and to or from another medium
- Every transfer is an output from one medium and an input into another. The medium can be a physical device, network, or files within a system
9. How is Node.js most frequently used?
Node.js is widely used in the following applications:
- Real-time chats
- Internet of Things
- Complex SPAs (Single-Page Applications)
- Real-time collaboration tools
- Streaming applications
- Microservices architecture
10. Explain the difference between frontend and backend development?
| Front-end | Back-end |
| Frontend refers to the client-side of an application | Backend refers to the server-side of an application |
| It is the part of a web application that users can see and interact with | It constitutes everything that happens behind the scenes |
| It typically includes everything that attributes to the visual aspects of a web application | It generally includes a web server that communicates with a database to serve requests |
| HTML, CSS, JavaScript, AngularJS, and ReactJS are some of the essentials of frontend development | Java, PHP, Python, and Node.js are some of the backend development technologies |
11. What is NPM?
NPM stands for Node Package Manager, responsible for managing all the packages and modules for Node.js.
Node Package Manager provides two main functionalities:
- Provides online repositories for node.js packages/modules, which are searchable on search.nodejs.org
- Provides command-line utility to install Node.js packages and also manages Node.js versions and dependencies
12. What are the modules in Node.js?
Modules are like JavaScript libraries that can be used in a Node.js application to include a set of functions. To include a module in a Node.js application, use the require() function with the parentheses containing the module’s name.
Node.js has many modules to provide the basic functionality needed for a web application. Some of them include:
| Core Modules | Description |
| HTTP | Includes classes, methods, and events to create a Node.js HTTP server |
| util | Includes utility functions useful for developers |
| fs | Includes events, classes, and methods to deal with file I/O operations |
| url | Includes methods for URL parsing |
| query string | Includes methods to work with query string |
| stream | Includes methods to handle streaming data |
| zlib | Includes methods to compress or decompress files |
13. What is the purpose of the module .Exports?
In Node.js, a module encapsulates all related codes into a single unit of code that can be parsed by moving all relevant functions into a single file. You may export a module with the module and export the function, which lets it be imported into another file with a needed keyword.
14. Why is Node.js preferred over other backend technologies like Java and PHP?
Some of the reasons why Node.js is preferred include:
- Node.js is very fast
- Node Package Manager has over 50,000 bundles available at the developer’s disposal
- Perfect for data-intensive, real-time web applications, as Node.js never waits for an API to return data
- Better synchronization of code between server and client due to same code base
- Easy for web developers to start using Node.js in their projects as it is a JavaScript library
15. What is the difference between Angular and Node.js?
| Angular | Node.js |
| It is a frontend development framework | It is a server-side environment |
| It is written in TypeScript | It is written in C, C++ languages |
| Used for building single-page, client-side web applications | Used for building fast and scalable server-side networking applications |
| Splits a web application into MVC components | Generates database queries |
16. Which database is more popularly used with Node.js?
MongoDB is the most common database used with Node.js. It is a NoSQL, cross-platform, document-oriented database that provides high performance, high availability, and easy scalability.
17. What are some of the most commonly used libraries in Node.js?
There are two commonly used libraries in Node.js:
- ExpressJS – Express is a flexible Node.js web application framework that provides a wide set of features to develop web and mobile applications.
- Mongoose – Mongoose is also a Node.js web application framework that makes it easy to connect an application to a database.
18. What are the pros and cons of Node.js?
| Node.js Pros | Node.js Cons |
| Fast processing and an event-based model | Not suitable for heavy computational tasks |
| Uses JavaScript, which is well-known amongst developers | Using callback is complex since you end up with several nested callbacks |
| Node Package Manager has over 50,000 packages that provide the functionality to an application | Dealing with relational databases is not a good option for Node.js |
| Best suited for streaming huge amounts of data and I/O intensive operations | Since Node.js is single-threaded, CPU intensive tasks are not its strong suit |
19. What is the command used to import external libraries?
The “require” command is used for importing external libraries. For example – “var http=require (“HTTP”).” This will load the HTTP library and the single exported object through the HTTP variable.
var http = require('http');Intermediate Node.js Interview Questions
20. What does event-driven programming mean?
An event-driven programming approach uses events to trigger various functions. An event can be anything, such as typing a key or clicking a mouse button. A call-back function is already registered with the element executes whenever an event is triggered.
21. What is an Event Loop in Node.js?
Event loops handle asynchronous callbacks in Node.js. It is the foundation of the non-blocking input/output in Node.js, making it one of the most important environmental features.
22. Differentiate between process.nextTick() and setImmediate()?
The distinction between method and product. This is accomplished through the use of nextTick() and setImmediate(). next Tick() postpones the execution of action until the next pass around the event loop, or it simply calls the callback function once the event loop’s current execution is complete, whereas setImmediate() executes a callback on the next cycle of the event loop and returns control to the event loop for any I/O operations.
23. What is an EventEmitter in Node.js?
- EventEmitter is a class that holds all the objects that can emit events
- Whenever an object from the EventEmitter class throws an event, all attached functions are called upon synchronously
const EventEmitter = require('events');
class MyEmitter extends EventEmitter { }
const myEmitter = new MyEmitter();
myEmitter.on('event',()=>{
console.log('an event occurred!');
});
myEmitter.emit('event');24. What are the two types of API functions in Node.js?
The two types of API functions in Node.js are:
- Asynchronous, non-blocking functions
- Synchronous, blocking functions
25. What is the package.json file?
The package.json file is the heart of a Node.js system. This file holds the metadata for a particular project. The package.json file is found in the root directory of any Node application or module
This is what a package.json file looks like immediately after creating a Node.js project using the command:
npm initYou can edit the parameters when you create a Node.js project.
{
"name": "node-npm",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "A demo application",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1"
},
"author": "Taha",
"license": "ISC"
}26. How would you use a URL module in Node.js?
The URL module in Node.js provides various utilities for URL resolution and parsing. It is a built-in module that helps split up the web address into a readable format.
var url = require('url');
var adrs = 'http://localhost:8080/default.htm?year=2020&month=march';
var que = url.parse(adrs, true);
console.log(que.host); //returns 'localhost:8080'
console.log(que.pathname); //returns /default.htm'
console.log(que.search); //returns "?year=2020 and month=march'
var quedata = que.query; //returns an object:{year: 2020,
month:'march'}
console.log(quedata.month); //returns 'march'27. What is the Express.js package?
Express is a flexible Node.js web application framework that provides a wide set of features to develop both web and mobile applications
28. How do you create a simple Express.js application?
- The request object represents the HTTP request and has properties for the request query string, parameters, body, HTTP headers, and so on
- The response object represents the HTTP response that an Express app sends when it receives an HTTP request
var express = require('express');
var app = express();
app.get('/", function (req, res) {
res.send('Hello World');
})
var server = app.listen(8081, function () {
var host = server.address().address
var port = servor.address().port
console.log("Example app listening at http://%s:%s", host, port)
})29. What are streams in Node.js?
Streams are objects that enable you to read data or write data continuously.
There are four types of streams:
Readable – Used for reading operations
Writable − Used for write operations
Duplex − Can be used for both reading and write operations
Transform − A type of duplex stream where the output is computed based on input
30. How do you install, update, and delete a dependency?
Install Dependency
PS C: \Users\Sam\Desktop\nodejs projects\mysql> npm install expressUpdate Dependency
PS C: \Users\Sam\Desktop\node js projects\mysql> npm updateUninstall Dependency
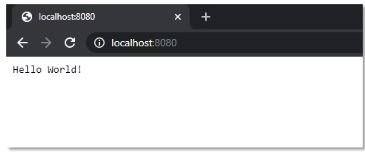
PS C: \Users\Sam\Desktop\nodejs projects\mysql> npm uninstall express31. How do you create a simple server in Node.js that returns Hello World?
var http = require('http');
http.createServer(function(req,res){
res.writeHead(200,{'Content-Type':'text/plain'});
res.end('Hello World\n');
}).listen(8080,'127.0.0.1');- Import the HTTP module
- Use createServer function with a callback function using request and response as parameters.
- Type “hello world.”
- Set the server to listen to port 8080 and assign an IP address
32. Explain asynchronous and non-blocking APIs in Node.js.
- All Node.js library APIs are asynchronous, which means they are also non-blocking
- A Node.js-based server never waits for an API to return data. Instead, it moves to the next API after calling it, and a notification mechanism from a Node.js event responds to the server for the previous API call
33. How do we implement async in Node.js?
As shown below, the async code asks the JavaScript engine running the code to wait for the request.get() function to complete before moving on to the next line for execution.
async function fun1(req, res){
let response = await request.get('http://localhost:3000');
if(response.err){console.log('error');)
else{console.log('fetched response');
}34. What is a callback function in Node.js?
A callback is a function called after a given task. This prevents any blocking and enables other code to run in the meantime.
In the last section, we will now cover some of the advanced-level Node.js interview questions.
Advanced Node.js Interview Questions
35. What is REPL in Node.js?
REPL stands for Read Eval Print Loop, and it represents a computer environment. It’s similar to a Windows console or Unix/Linux shell in which a command is entered. Then, the system responds with an output
REPL performs the following desired tasks:
- Read – Reads user’s input, parses the input into JavaScript data structure and stores it in memory
- Eval – Takes and evaluates the data structure
- Print – Prints the result
- Loop – Loops the above command until user presses ctrl-c twice
36. What is the control flow function?
The control flow function is a piece of code that runs in between several asynchronous function calls.
37. How does control flow manage the function calls?
The Control Flow does the following jobs:
- Control the order of execution
- Collect data
- Limit concurrency
- Call the next step in a program
38. What is the difference between fork() and spawn() methods in Node.js?
| fork() | spawn() |
| fork() is a particular case of spawn() that generates a new instance of a V8 engine. | Spawn() launches a new process with the available set of commands. |
| Multiple workers run on a single node code base for multiple tasks. | This method doesn’t generate a new V8 instance, and only a single copy of the node module is active on the processor. |
39. What is the buffer class in Node.js?
Buffer class stores raw data similar to an array of integers but corresponds to a raw memory allocation outside the V8 heap. Buffer class is used because pure JavaScript is not compatible with binary data
40. What is piping in Node.js?
Piping is a mechanism used to connect the output of one stream to another stream. It is normally used to retrieve data from one stream and pass output to another stream
41. What are some of the flags used in the read/write operations in files?
- r – Open file for reading. An exception occurs if the file does not exist.
- r+ – Open file for reading and writing. An exception occurs if the file does not exist.
- w – Open file for writing. The file is created (if it does not exist) or truncated (if it exists).
- w+ – Open file for reading and writing. The file is created (if it does not exist) or truncated (if it exists).
- a – Open file for appending. The file is created if it does not exist.
- at – Open file for reading and appending. The fileis created if it does not exist.
42. How do you open a file in Node.js?
This is the syntax for opening a file in Node.js
fs.open(path, flags[, mode], callback)43. What is callback hell?
- Callback hell, also known as the pyramid of doom, is the result of intensively nested, unreadable, and unmanageable callbacks, which in turn makes the code harder to read and debug
- improper implementation of the asynchronous logic causes callback hell
44. What is a reactor pattern in Node.js?
A reactor pattern is a concept of non-blocking I/O operations. This pattern provides a handler that is associated with each I/O operation. As soon as an I/O request is generated, it is then submitted to a demultiplexer
45. What is a test pyramid in Node.js?

A test pyramid is a figure which explains the proportion of unit tests, integrations tests, and end-to-end tests that are required for the proper development of a project.
The components of a test pyramid are given below:
- Unit Tests: They test the individual units of code in isolation
- Integrations Tests: They test the integration among dissimilar units
- End-to-End (E2E) Tests: They test the whole system, from the User Interface to the data store, and back.
46. For Node.js, why does Google use the V8 engine?
The V8 engine, developed by Google, is open-source and written in C++. Google Chrome makes use of this engine. V8, unlike the other engines, is also utilized for the popular Node.js runtime. V8 was initially intended to improve the speed of JavaScript execution within web browsers. Instead of employing an interpreter, V8 converts JavaScript code into more efficient machine code to increase performance. It turns JavaScript code into machine code during execution by utilizing a JIT (Just-In-Time) compiler, as do many current JavaScript engines such as SpiderMonkey or Rhino (Mozilla).
47. Describe Node.js exit codes.
Exit codes are a set of specific codes which are used for finishing a specific process. Given below are some of the exit codes used in Node.js:
- Uncaught fatal exception
- Unused
- Fatal Error
- Internal Exception handler Run-time failure
- Internal JavaScript Evaluation Failure
48. Explain the concept of middleware in Node.js.
Middleware is a function that receives the request and response objects. Most tasks that the middleware functions perform are:
- Execute any code
- Update or modify the request and the response objects
- Finish the request-response cycle
- Invoke the next middleware in the stack
49. What are the different types of HTTP requests?
HTTP defines a set of request methods used to perform desired actions. The request methods include:
GET: Used to retrieve the data
POST: Generally used to make a change in state or reactions on the server
HEAD: Similar to the GET method, but asks for the response without the response body
DELETE: Used to delete the predetermined resource
50. How would you connect a MongoDB database to Node.js?
To create a database in MongoDB:
- Start by creating a MongoClient object
- Specify a connection URL with the correct IP address and the name of the database you want to create
var MongoClient = require('mongodb').MongoClient;
var url = "mongodb://localhost:27017/mydb";
MongoClient.connect(url, function(err, db) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log("Database created!");
db.close();
});51. What is the purpose of NODE_ENV?
- NODE ENV is an environmental variable that stands for node environment in express server
- It’s how we set and detect which environment we are in
export NODE_ENV=production52. What is WASI, and why is it being introduced?
The WASI class implements the WASI system called API and extra convenience methods for interacting with WASI-based applications. Every WASI instance represents a unique sandbox environment. Each WASI instance must specify its command-line parameters, environment variables, and sandbox directory structure for security reasons.
53. What are LTS releases of Node.js?
LTS stands for Long Term Support version of Node.js that receives all the critical bug fixes along with security updates and performance improvements. These versions are supported for at least 18 months and mainly focus on stability and security. The modifications done to the LTS versions are restricted to bug fixes, security upgrades, npm, documentation updates, performance improvement, etc.